ARTICLE AD BOX
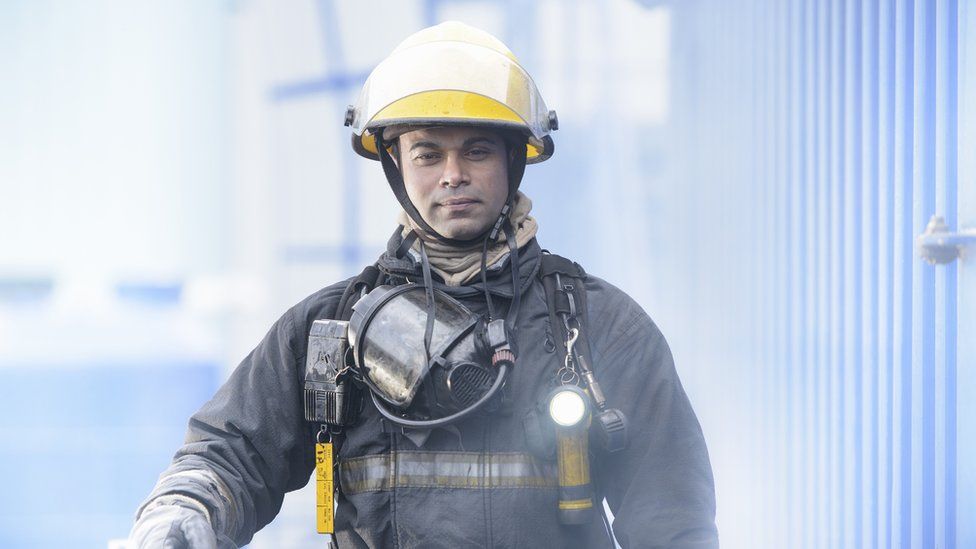

Tougher rules for some workers planning strike action have been announced by the government.
It said the move will ensure key services like the NHS are protected, but unions are expected to take legal action.
How could strike rules change?
Under the proposals some trade union members would be required to continue working during a strike.
This would be to ensure a "minimum level of service".
The sectors covered by the plans are:
- The NHS
- Transport
- Education
- Fire and rescue
- Border security
- Nuclear decommissioning
The government said it would consult on the minimum level of staffing for the fire and ambulance services, as well as the railways.
It said it expects to be able to reach voluntary agreements about workers in other affected roles.
The government said it intends to introduce the measures in the coming weeks. However, they will still need to be agreed by MPs and Lords before becoming law.
Business Secretary Grant Shapps said the move would protect the public from disproportionate disruption caused by strikes. Unions, however, said it would do nothing to resolve current disputes.
Labour leader Sir Keir Starmer said any such laws brought in by the current government would be abolished if it won the next election.
Is anyone allowed to strike at present?
A few professions are already not allowed to strike.
Police officers, for example, are banned from taking strike action.
Nurses have an agreement that they should only walk out if it does not risk the wellbeing of patients.
Non-union members can also strike, says Crystal Boyde, an employment lawyer at Thrive Law.
"As long as the industrial action is lawful, non-union members are allowed to go on strike and remain protected from dismissal," she says.
What are the current rules for calling a strike?
The law says a strike can only happen if a majority of union members agree via an organised vote - known as a ballot.
There are strict rules around holding a vote. For example, it must be a postal ballot - where members vote on paper and return it in a prepaid envelope.
If workers agree to strike, details must be given to the employer at least 14 days before it begins (unless the union and employer agree to seven days).
If the rules aren't followed, a court could prevent a strike taking place. In 2010, for example, BA won a High Court injunction to stop strikes by cabin staff.
Can strikers be sacked or replaced at present?
UK employees are protected from being sacked during the first 12 weeks of any official industrial action.
If a worker is sacked during this period, they can claim unfair dismissal.
However, workers can be dismissed after 12 weeks if the employer has tried to settle the dispute. For example, if an employment adviser like Acas has been brought in to help find a solution.
The government has introduced a new law allowing businesses to use agency workers to fill in for striking workers.
However, 11 trade unions have mounted a legal challenge, saying the move undermines workers' right to strike.
What is a trade union?
Trade unions are organisations which help workers negotiate with employers.
They often help employees ask for more pay, or better working conditions. Unions also represent members who have problems at work, or who are facing a disciplinary procedure.
If negotiations with employers don't work, a trade union's members might decide to take action such as a strike.
How many people are in trade unions?
Unions exist across many industries, including firefighting, teaching and transport. Members normally pay a monthly subscription and can leave at any point.
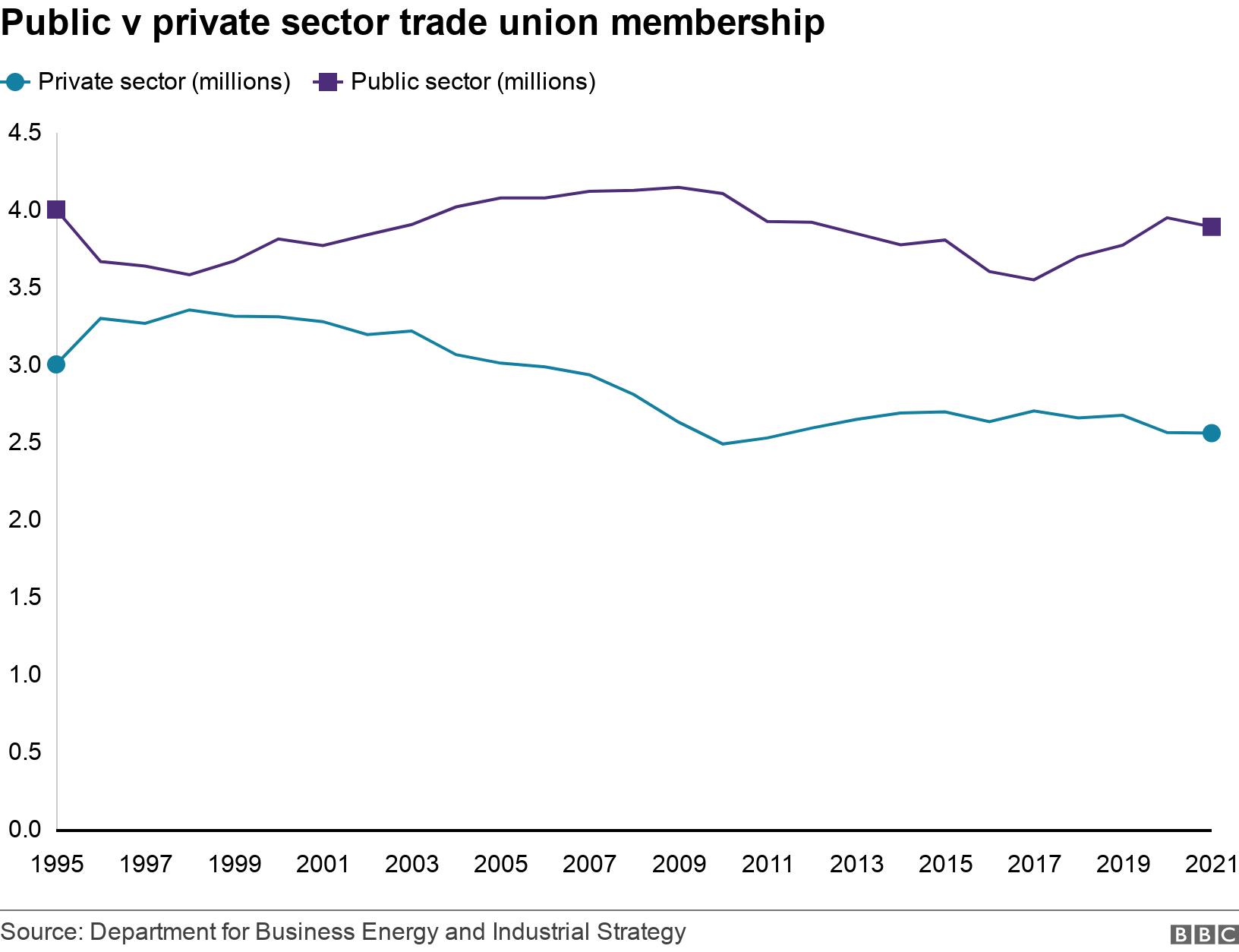
Almost one in four UK workers (23%) were union members in 2021 - a total of 6.4 million people, according to government statistics.
After peaking at 13.2 million in 1979, union membership has fallen significantly - although the rate of decline has slowed.
In 2021, 50% of public sector workers - including people like teachers and health workers - were in a union, compared with 13% of private sector employees. Employees over 50 are most likely to be members.
Are strikers paid and can they still choose to work?
Workers on strike can expect to lose wages for the time they do not work.
No-one can be forced to take part in a strike - so a worker can still choose to work.
Image source, Getty Images
Image caption,Picket lines are common sights during strikes
How are trade unions linked to the Labour Party?
The Labour Party was created from the trade union movement in 1900 and still retains close links.
There are currently 12 trade unions affiliated to the party, including two of the largest - Unison and Unite.
Labour relies on the unions for funding. During the last general election campaign Labour received a total of £5.4m - of which £5m came from trade union donations.
Members of trade unions linked to Labour can apply to be allowed to vote in party leadership elections.

 1 year ago
86
1 year ago
86








 English (US)
English (US)